
Many think using a proxy or VPN is enough to stay anonymous online. However, these tools only hide your IP address. Websites have other ways to identify users, one of which is through a digital fingerprint, a unique combination of device and browser settings.
In this article, we’ll explain what a digital fingerprint is, how it’s used, and how you can protect yourself from being tracked based on it.
Websites aim to identify their users so they can gather information from the devices accessing them. They analyze various data points, from obvious ones like geolocation to less expected details like the fonts installed on your system. Together, all these parameters create what we call a digital fingerprint.
For example, imagine you have an M1-based MacBook Air, live in the UTC -5 timezone, and use Safari version 16.5.2. While each parameter is standard among many users, combining all three is much rarer. When you combine all these details, you create a nearly unique fingerprint that can identify you with about 94% accuracy.
Initially, websites gathered detailed information about user devices to ensure proper rendering. Devices differ in screen size, resolution, color depth, and other hardware characteristics, so web pages need to adapt to each gadget. For instance, when you access a site from your smartphone, you see the mobile version rather than the desktop one. The site determines this based on your digital fingerprint.
Today, digital fingerprints serve other important purposes as well. They help identify visitors to protect online resources from bots and hackers. If you’ve ever faced CAPTCHAs after making several requests to a website, that’s the anti-fraud system suspecting your activity might be automated.
Additionally, these systems help prevent multi-accounting, where a single user creates multiple accounts, violating platform rules. This is often prohibited on social media and marketplaces, as it allows for manipulating subscriber activity or posting fake reviews.
In short, digital fingerprints are mainly used to ensure proper website rendering across different devices, protect against bots and hackers, and prevent multi-accounting.
The most straightforward way to change your digital fingerprint might seem like switching devices or relocating to a different city or country. However, that’s not practical for most people seeking online anonymity.
A more straightforward method involves adjusting system settings on your phone or laptop. You can change your device’s language, timezone, and screen resolution. Additionally, deleting old fonts, downloading new ones, and removing installed browser extensions can help. While it’s possible to change hardware characteristics by buying new components like a GPU or hard drive, this is only sometimes cost-effective, and you might still have some fingerprint parameters that can’t be changed.
What about using a VPN or a proxy? While these tools can mask your IP address, they don’t alter your digital fingerprint. This might work if you only need to access a blocked website in your region. However, for complete anonymity or multi-accounting purposes, you must also change all other fingerprint parameters.
This is where dedicated multi-accounting anti-detect browsers, like Octo Browser, come in. These browsers function like regular options such as Google Chrome or Firefox, but they focus on enhancing user anonymity instead of collecting data for advertising. For instance, Octo Browser spoofs the fingerprint at the kernel level, which helps avoid website detection.

New users can use the promo code CLIPROXY30 for a 30% discount for the first payment.
Don’t miss this opportunity to elevate your digital fingerprint game
Digital fingerprints vary across websites, depending on how their anti-fraud systems work. In tools like Octo Browser, you can configure over 50 different fingerprint parameters. Here are some key components:
These parameters together create a digital fingerprint that can be used for tracking and identification online. Adjusting them thoughtfully can enhance your online anonymity.
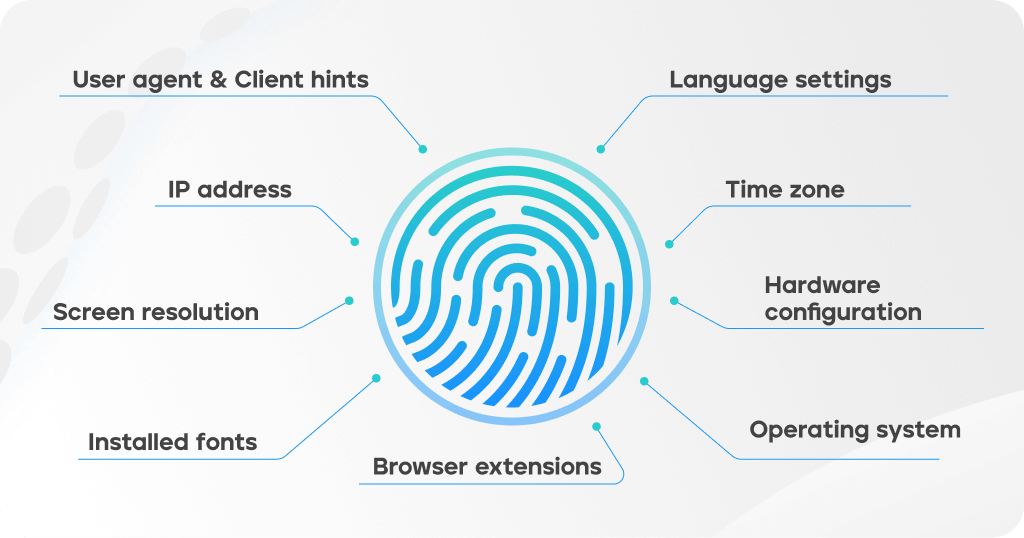
Websites closely monitor digital fingerprints to detect and block potentially suspicious activity. Several factors can lead to a ban:
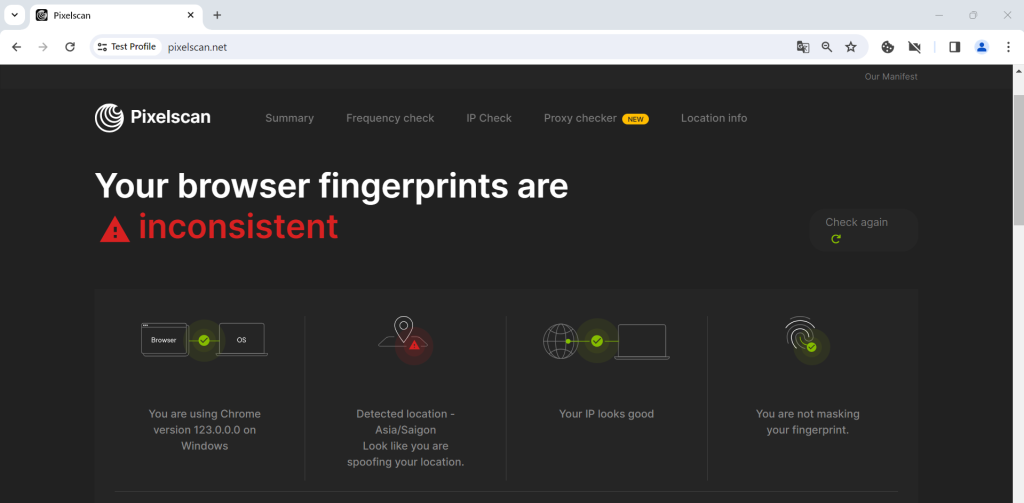
1. Inconsistent Digital Fingerprint: Websites evaluate how well various fingerprint parameters align. If there’s a mismatch, it raises suspicion. For instance, the discrepancy will be evident if you change your location to Vietnam in your anti-detect browser but continue using your actual IP address. The website will notice the inconsistency between the IP location and the location set in the browser, which can trigger a ban.
2. Uniqueness of the Fingerprint: A digital fingerprint should resemble those of typical users to avoid drawing attention. If most of your parameters indicate you’re using a shared device, but one or two are unusual, it can be flagged. For example, suppose your settings show you’re using an HP laptop with a standard screen resolution and operating system. Still, you have an uncommon font like San Francisco (which is typically associated with Apple products). In that case, this unusual combination makes your fingerprint more unique and suspicious.
3. Unreliable IP Address: Websites often block access based on the reputation of your IP address. If your IP is associated with a data center or appears on a blacklist, the website may restrict your access. This is why using reliable, high-quality proxies is essential for scraping and maintaining anonymity.
To avoid triggering bans, ensure that your digital fingerprint is consistent, typical, and associated with a trustworthy IP address.
To see what your digital fingerprint looks like, you can use various online checker services like Pixelscan, Browserleaks, or CreepJs. Simply visit these sites using the device and browser you want to analyze. They will display the settings visible to websites and assess the uniqueness and consistency of your fingerprint. This can be especially useful for testing how well your anti-detect browser is functioning.
A VPN only changes your IP address and does not alter any other parameters of your browser fingerprint. Therefore, relying solely on a VPN will not be sufficient to bypass fingerprint-based bans. If your IP address does not match the location indicated by your fingerprint settings, anti-fraud systems will likely flag your activity as suspicious.
Incognito mode can be helpful when multiple users share a single device and want to keep their activities private. In this mode, cookies, browsing history, and form data are not saved on the device. However, websites can still detect your device parameters and identify you. If you’re curious about the difference, you can visit a fingerprint checker in a regular browser window and in incognito mode to compare the results. You’ll likely find the device parameters still visible even in incognito mode.
Fingerprint spoofing provides several advantages:
The impact of poorly executed fingerprint spoofing largely depends on the platform’s rules and anti-fraud measures. For casual browsing, you might not encounter significant issues using an anti-detect browser. However, for multi-accounting, the quality of spoofing becomes crucial.
Platforms like social media and marketplaces are generally against multi-accounting. While having separate stores for different brands on Amazon is typically acceptable, if the platform suspects you’re manipulating sales figures or reviews, all related accounts could be banned, and recovery may be difficult.
In summary, reliable multi-accounting anti-detect browsers that provide high-quality fingerprint spoofing are essential. Tools like Octo Browser can create profiles that pass the most popular fingerprint checkers, ensuring a safer multi-accounting experience.


